Rheumatoid Arthritis
Table of Contents
Introduction
Rheumatoid Arthritis is a persistent autoimmune condition that predominantly impacts the joints, resulting in discomfort, inflammation, and rigidity. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a persistent autoimmune condition impacting millions of individuals globally. It is crucial to understand the intricacies of this condition to ensure early detection and effective management.
Definition and Background
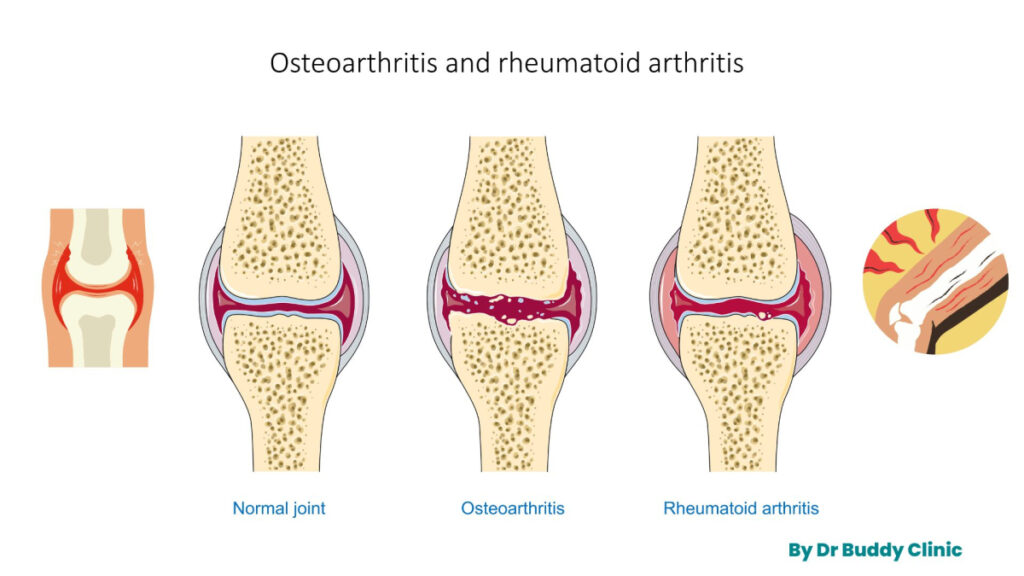
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is caused by wear and tear, RA occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation in the joints. This abnormal immune response can also affect other organs, such as the heart, lungs, and eyes.
RA is more common in women, with a higher prevalence observed in individuals between the ages of 30 and 60. However, it has the potential to impact individuals across all age groups and genders.. The exact cause of RA remains unknown, although genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a significant role.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
To comprehend the complexities of rheumatoid arthritis, let’s delve into its definition, classification, causes, and risk factors.
Definition and Classification
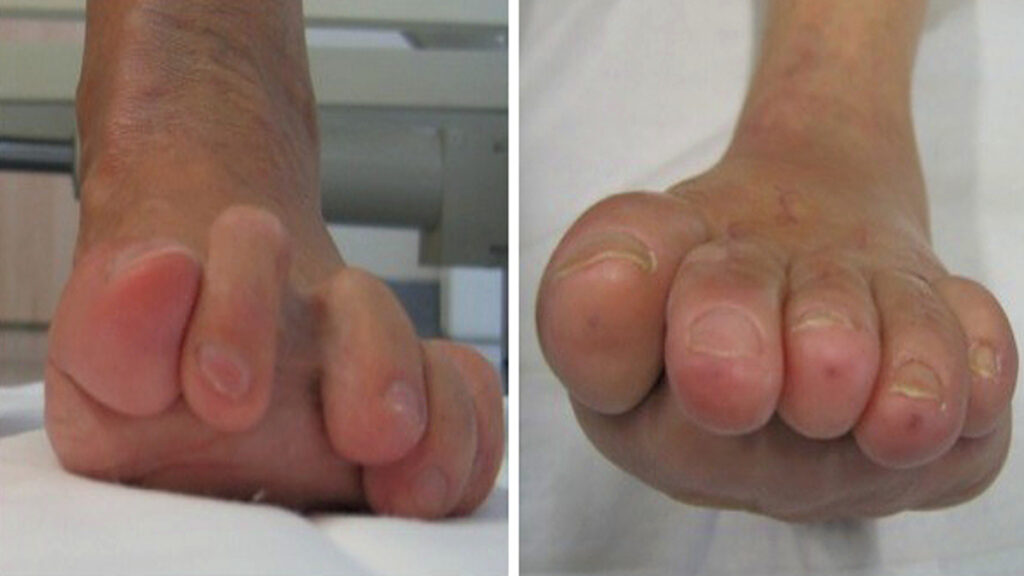
Rheumatoid arthritis is classified as a chronic inflammatory arthritis and is one of the most common autoimmune diseases. It falls into the category of connective tissue diseases, characterized by persistent inflammation in the lining of the joints. The inflammation eventually leads to joint deformities and erosion of surrounding tissues.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of RA is still under investigation. However,studies indicate that the development of this condition is influenced by a blend of genetic and environmental factors. Certain genes may increase an individual’s susceptibility to RA, while environmental triggers such as smoking, infections, or hormonal changes can initiate the disease. Additionally, a family history of RA and gender can also affect the risk of developing this condition.
Pathophysiology Explained
In rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium, a thin membrane that lines the joints. This triggers an inflammatory response, leading to the release of various chemicals and enzymes that damage the cartilage, bones, and surrounding tissues. The continuous inflammation results in a progressive cycle of joint destruction and stimulates the growth of abnormal tissue called pannus. The pannus further exacerbates the destruction of the joint, causing pain and loss of function.
Recognizing Symptoms and Diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Early detection and diagnosis play a crucial role in effectively managing rheumatoid arthritis. Let’s discuss the early warning signs, common symptoms, and diagnostic tests.
Early Warning Signs
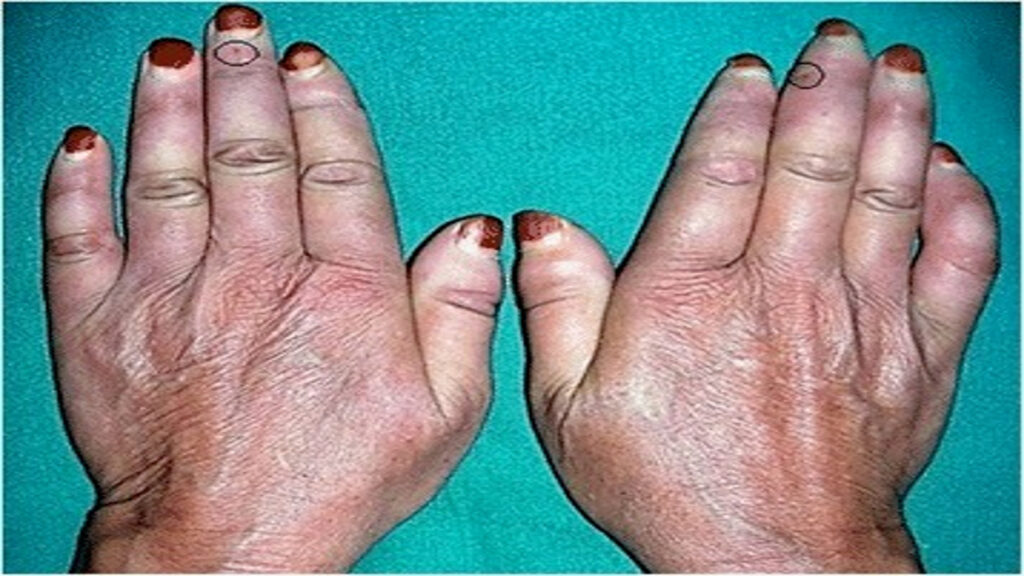
Rheumatoid arthritis often begins with subtle warning signs that may be overlooked or attributed to other causes. Fatigue, morning stiffness, and generalized aches are early indicators of the disease. It is essential to pay attention to these symptoms, especially if they persist for several weeks or months.
Common Symptoms and Their Impact
As rheumatoid arthritis progresses, symptoms may become more pronounced and disruptive. Joint pain, swelling, and stiffness are commonly experienced, particularly in the hands, wrists, and knees. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s ability to perform daily activities, leading to decreased mobility and reduced quality of life.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
To confirm a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis, healthcare professionals employ various tests and procedures. These may include blood tests to assess for elevated levels of specific antibodies and markers of inflammation. Imaging techniques such as X-rays or ultrasound can also provide valuable insights into joint damage and inflammation.
Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Managing rheumatoid arthritis requires a comprehensive treatment approach. Let’s explore the available options, including medications, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and surgical interventions.
Medications: DMARDs, NSAIDs, Biologic Response Modifiers
Medications play a crucial role in controlling inflammation, reducing pain, and slowing the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are commonly prescribed to suppress the immune response and prevent joint damage. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) offer alleviation from both pain and inflammation. Biologic response modifiers target specific components of the immune system, offering targeted therapy for RA.
These medications work by inhibiting the production of certain chemicals in the body that contribute to pain and inflammation. By doing so, NSAIDs not only provide relief but also contribute to improved mobility and enhanced overall comfort for individuals dealing with conditions like Rheumatoid Arthritis.
It’s important to note that while NSAIDs can be effective, they are not without potential side effects. Common side effects may include gastrointestinal issues, such as stomach upset or ulcers, and, in some cases, they may impact kidney function. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals to use NSAIDs under the guidance of healthcare professionals who can tailor the treatment plan to minimize risks and maximize benefits.
In addition to pharmaceutical interventions, complementary approaches like physical therapy and lifestyle modifications can further enhance the management of pain and inflammation associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Physical therapy exercises, designed to improve joint flexibility and strength, play a pivotal role in promoting overall joint health.
Furthermore, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, regular exercise, and stress management techniques, can significantly contribute to the holistic well-being of individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis. These lifestyle adjustments not only support the effectiveness of medical treatments but also empower individuals to actively participate in their own health and wellness journey.
Physical Therapy and Occupational Therapy
Physical and occupational therapy are essential components of rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Physical therapy aims to improve joint mobility, strengthen muscles, and alleviate pain through therapeutic exercises and modalities. Occupational therapy focuses on adapting daily activities and providing assistive devices to enhance independence and productivity.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases where other treatments fail to provide adequate relief, surgical interventions may be necessary. Joint replacement surgeries, such as hip or knee replacements, can significantly improve mobility and reduce pain in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
In addition to medical interventions, several lifestyle modifications and strategies can help manage rheumatoid arthritis effectively.
Lifestyle Modifications: Exercise, Diet, and Weight Management
Regular exercise, tailored to an individual’s abilities and preferences, can help maintain joint flexibility, muscle strength, and overall physical well-being. Additionally, following a well-balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can support overall health and minimize inflammation. Weight management is also crucial, as excess weight can aggravate joint pain and strain.
Pain Management Strategies
Managing pain is a critical aspect of living with rheumatoid arthritis. Apart from medications, individuals can explore alternative pain management strategies, such as heat or cold therapy, acupuncture, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). Psychological techniques like mindfulness meditation and relaxation exercises may also help reduce pain perception.
Emotional Support and Coping Mechanisms
The emotional toll of rheumatoid arthritis should not be underestimated. Seeking emotional support from loved ones, participating in support groups, or engaging in counseling sessions can provide a much-needed outlet for emotional relief. Developing effective coping mechanisms, such as practicing stress-management techniques or engaging in hobbies, can also enhance overall well-being.
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with rheumatoid arthritis presents unique challenges. Let’s examine how individuals can enhance their quality of life, manage their workload, and navigate relationships and family planning.
Enhancing Quality of Life
Managing rheumatoid arthritis can significantly improve one’s quality of life. Adapting living spaces, such as installing grab bars or using assistive devices, can facilitate independence and enhance safety. Engaging in activities that bring joy and purpose can also contribute to a fulfilling life despite the challenges posed by the condition.
Maintaining Employment and Managing Workload
Having rheumatoid arthritis does not necessarily mean giving up on work or career aspirations. Open communication with employers, exploring workplace accommodations, and pacing oneself can help individuals with RA maintain employment while effectively managing their workload. Prioritizing self-care and ensuring a healthy work-life balance are also essential in minimizing the impact on professional life.
Relationships, Pregnancy, and Family Planning
Rheumatoid arthritis can influence relationships and family planning decisions. Open and honest communication with partners and family members is crucial to ensure support and understanding. Planning for pregnancy may require coordination with healthcare professionals, as certain medications used to manage RA may need to be adjusted to support a healthy pregnancy. Seeking advice from healthcare providers with expertise in managing rheumatic diseases during pregnancy is vital to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Summary and Conclusion
In conclusion, rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the joints, leading to pain, inflammation, and stiffness. Early detection and comprehensive treatment are vital in effectively managing the condition and minimizing its impact on daily life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis can take control of their health and enhance their overall well-being.
Looking Towards the Future
Continued research into the understanding and management of rheumatoid arthritis holds promise for improved treatment modalities and outcomes. Advancements in personalized medicine, including targeted therapies and precision medicine approaches, may revolutionize the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Collaborative efforts between healthcare professionals, researchers, and individuals with rheumatoid arthritis will continue to drive progress in the field.
Importance of Early Detection and Comprehensive Treatment
Early detection of rheumatoid arthritis is crucial to prevent irreversible joint damage and disability. Comprehensive treatment approaches that include a combination of medication, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and lifestyle modifications offer the best chance for successful management of the disease. Individuals experiencing symptoms should seek medical attention promptly to receive an accurate diagnosis and begin appropriate treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Let’s address some common questions regarding rheumatoid arthritis.
How does rheumatoid arthritis differ from osteoarthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are both types of arthritis, but they differ in several ways. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, whereas osteoarthritis is caused by wear and tear on the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis typically involves multiple joints symmetrically, while osteoarthritis usually affects specific joints asymmetrically.
Can rheumatoid arthritis be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis. However, with early detection and comprehensive treatment, it is possible to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and slow down the progression of the disease.
How can I manage the pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis?
Pain management strategies for rheumatoid arthritis include medications, alternative therapies, and lifestyle modifications. Working closely with healthcare professionals to find the most effective combination of treatments tailored to individual needs is essential in managing pain.
What alternative therapies are available for rheumatoid arthritis?
Although alternative therapies have shown promise in managing rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals before incorporating them into one’s treatment plan. Some alternative therapies that individuals with rheumatoid arthritis may consider include acupuncture, massage therapy, and herbal supplements.
Can pregnancy affect rheumatoid arthritis symptoms?
Pregnancy can have varying effects on rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Some women experience an improvement in symptoms during pregnancy, while others may experience a flare-up. It is important for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a management plan that ensures the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Is it possible to prevent the onset of rheumatoid arthritis?
Currently, there is no surefire way to prevent the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a well-balanced diet, and avoiding smoking, may reduce the risk of developing the disease. Additionally, early detection and treatment of warning signs can help minimize the impact of rheumatoid arthritis on individuals’ lives.
With comprehensive knowledge about rheumatoid arthritis, its symptoms, and management strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their quality of life and minimize the impact of the disease. Remember, early detection, proper treatment, and ongoing support are key in managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively.
Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis :
In addition to medical interventions, several lifestyle modifications and strategies can help manage rheumatoid arthritis effectively.
Lifestyle Modifications: Exercise, Diet, and Weight Management :
Regular exercise, tailored to an individual’s abilities and preferences, can help maintain joint flexibility, muscle strength, and overall physical well-being. Additionally, following a well-balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can support overall health and minimize inflammation. Weight management is also crucial, as excess weight can aggravate joint pain and strain.
Pain Management Strategies :
Managing pain is a critical aspect of living with rheumatoid arthritis. Apart from medications, individuals can explore alternative pain management strategies, such as heat or cold therapy, acupuncture, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). Psychological techniques like mindfulness meditation and relaxation exercises may also help reduce pain perception.
Emotional Support and Coping Mechanisms :
The emotional toll of rheumatoid arthritis should not be underestimated. Seeking emotional support from loved ones, participating in support groups, or engaging in counseling sessions can provide a much-needed outlet for emotional relief. Developing effective coping mechanisms, such as practicing stress-management techniques or engaging in hobbies, can also enhance overall well-being.
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis :
Living with rheumatoid arthritis presents unique challenges. Let’s examine how individuals can enhance their quality of life, manage their workload, and navigate relationships and family planning.
Enhancing Quality of Life :
Managing rheumatoid arthritis can significantly improve one’s quality of life. Adapting living spaces, such as installing grab bars or using assistive devices, can facilitate independence and enhance safety. Engaging in activities that bring joy and purpose can also contribute to a fulfilling life despite the challenges posed by the condition.
Maintaining Employment and Managing Workload :
Having rheumatoid arthritis does not necessarily mean giving up on work or career aspirations. Open communication with employers, exploring workplace accommodations, and pacing oneself can help individuals with RA maintain employment while effectively managing their workload. Prioritizing self-care and ensuring a healthy work-life balance are also essential in minimizing the impact on professional life.
Relationships, Pregnancy, and Family Planning :
Rheumatoid arthritis can influence relationships and family planning decisions. Open and honest communication with partners and family members is crucial to ensure support and understanding. Planning for pregnancy may require coordination with healthcare professionals, as certain medications used to manage RA may need to be adjusted to support a healthy pregnancy. Seeking advice from healthcare providers with expertise in managing rheumatic diseases during pregnancy is vital to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Summary and Conclusion
In conclusion, rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the joints, leading to pain, inflammation, and stiffness. Early detection and comprehensive treatment are vital in effectively managing the condition and minimizing its impact on daily life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis can take control of their health and enhance their overall well-being.
Looking Towards the Future :
Continued research into the understanding and management of rheumatoid arthritis holds promise for improved treatment modalities and outcomes. Advancements in personalized medicine, including targeted therapies and precision medicine approaches, may revolutionize the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Collaborative efforts between healthcare professionals, researchers, and individuals with rheumatoid arthritis will continue to drive progress in the field.
Significance of Early Identification and Comprehensive Treatment?
Early detection of rheumatoid arthritis is crucial to prevent irreversible joint damage and disability. Comprehensive treatment approaches that include a combination of medication, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and lifestyle modifications offer the best chance for successful management of the disease. Individuals experiencing symptoms should seek medical attention promptly to receive an accurate diagnosis and begin appropriate treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Common Questions
How does rheumatoid arthritis differ from osteoarthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are both types of arthritis, but they differ in several ways. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, whereas osteoarthritis is caused by wear and tear on the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis typically involves multiple joints symmetrically, while osteoarthritis usually affects specific joints asymmetrically.
Can rheumatoid arthritis be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis. However, with early detection and comprehensive treatment, it is possible to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and slow down the progression of the disease.
How can I manage the pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis?
Pain management strategies for rheumatoid arthritis include medications, alternative therapies, and lifestyle modifications. Working closely with healthcare professionals to find the most effective combination of treatments tailored to individual needs is essential in managing pain.
What alternative therapies are available for rheumatoid arthritis?
Although alternative therapies have shown promise in managing rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals before incorporating them into one’s treatment plan. Some alternative therapies that individuals with rheumatoid arthritis may consider include acupuncture, massage therapy, and herbal supplements.
Can pregnancy affect rheumatoid arthritis symptoms?
Pregnancy can have varying effects on rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Some women experience an improvement in symptoms during pregnancy, while others may experience a flare-up. It is important for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a management plan that ensures the well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Is it possible to prevent the onset of rheumatoid arthritis?
Currently, there is no surefire way to prevent the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a well-balanced diet, and avoiding smoking, may reduce the risk of developing the disease. Additionally, early detection and treatment of warning signs can help minimize the impact of rheumatoid arthritis on individuals’ lives.

1 thought on “Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options”